Learning Modules
Module 02
Vaccine information
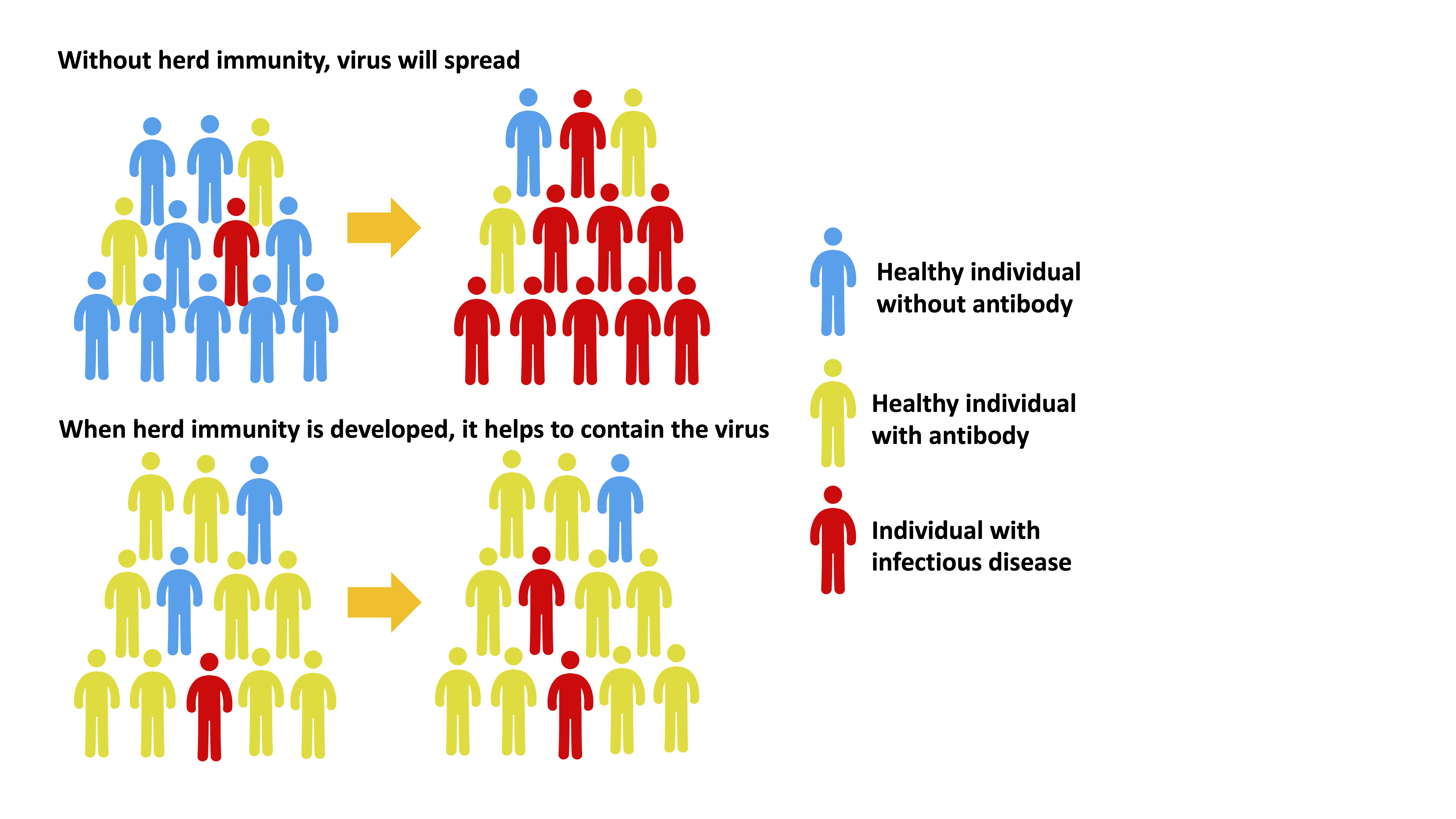
01. Vaccination and herd immunity
Herd immunity, also known as community immunity, occurs when a sufficient number of people in the community are immune to the pathogen causing the disease so that other non-immune individuals are protected from infection. The herd immunity theory suggests that when a large number of individuals in a group are immune to an infectious disease or when there are few susceptible individuals, the chain of infection of those infectious diseases that are transmitted between individuals will be interrupted.
02. Vaccines for three common infectious respiratory diseases
| Types of vaccines | Mechanism of action | Brand | Characteristics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inactivated or attenuated vaccine | Inactivated or attenuated virues are used. It can produce an immune response and does not cause a disease | COVID-19 | Influenza | Pneumococcal Infection |
|
|
|
|
|||
| RNA and DNA vaccines | Deliver viral RNA/DNA to the human body. The body cells are taught to prroduce their own SARSCoV2 protein fragments (vaccine antigens), which can induce an immune response in the body |
|
|||
03. Vaccine development and principles
3.1 Vaccine development:
Generally, an experimental vaccine is tested in human clinical trials in four phases.

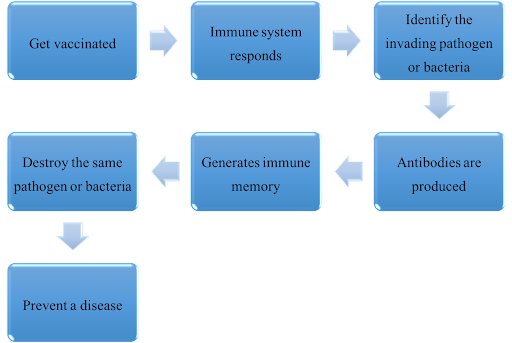
3.2 How the vaccines work:
04. Vaccines for three common infectious respiratory diseases in Hong Kong and their modes of administration
4.1 Coronavirus disease 2019
| For CoronaVac (Sinovac) vaccine: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age group | Number of doses and intervals | ||||
| 1st dose | Interval | 2nd dose | Interval | 3rd doses | |
| 18 - 49 years old | Recommended | 28 days | Recommended | 90 days | Recommended |
| 50 years of above | |||||
| Immunocompromised✽ | 28 days | ||||
*Immunocompromised persons include:
- Cancer or hematological malignancy on active immunosuppressive treatment now or in the past 12 months
- Recipients of solid organ transplant or stem cell transplant on immunosuppressive treatment
- Severe primary immunodeficiency or on chronic dialysis
- Advanced or untreated HIV disease
- On active immunosuppressive drugs, or immunosuppressive chemotherapy / radiotherapy in past 6 months
This table was updated on 18 October 2023, for real-time information, please see: https://www.covidvaccine.gov.hk/pdf/covid19vaccinationfactsheet_coronavac_eng.pdf
| For BioNTech vaccine: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age group | Number of doses and intervals | |||||
| 1st dose | Interval | 2nd dose | Interval | 3rd doses | ||
| 18- 49 years | Recommended | 56 days# | Recommended | 90 days | Recommended | |
| 50 years or above | 28 days# | 90 days | ||||
| Immunocompromised✽ | 28 days# | 28 days | ||||
*Immunocompromised persons include:
- Cancer or hematological malignancy on active immunosuppressive treatment now or in the past 12 months
- Recipients of solid organ transplant or stem cell transplant on immunosuppressive treatment
- Severe primary immunodeficiency or on chronic dialysis
- Advanced or untreated HIV disease
- On active immunosuppressive drugs, or immunosuppressive chemotherapy / radiotherapy in past 6 months
#This dosing interval could be shortened to a minimum of three weeks for those with personal needs under informed consent after consideration of individual risk and benefit.
This table was updated on 18 October 2023, for real-time information, please see: https://www.covidvaccine.gov.hk/pdf/covid19vaccinationfactsheet_coronavac_eng.pdf
The Hong Kong Government's arrangements for the additional vaccine booster of COVID-19 in 2023:
|
Citizens belonging to the following priority groups:
Citizens belonging to the following priority groups, if they have completed the initial doses, they can receive an additional vaccine booster at least 180 days after their last dose or recovery from COVID-19 infection (whichever is later) free of charge, regardless of the number of vaccine doses they received in the past:
|
Citizens belonging to other groups:
An additional booster may be considered at least 180 days after the last dose / recovery from COVID-19 infection (whichever is later) for the following groups of citizens based on personal choice as recommended by experts if they have completed the initial doses. They will need to get the vaccine in the private market at their own expense.
|
|---|---|
|
|
*Immunocompromised persons include:
- Cancer or hematological malignancy on active immunosuppressive treatment now or in the past 12 months;
- Recipients of solid organ transplant or stem cell transplant on immunosuppressive treatment;
- Severe primary immunodeficiency or on chronic dialysis;
- Advanced or untreated HIV disease;
- On active immunosuppressive drugs, or immunosuppressive chemotherapy / radiotherapy in past 6 months
^ Persons with underlying comorbidities:
- Chronic cardiovascular (except hypertension without complications), lung diseases
- Metabolic or kidney diseases, obesity (Body Mass Index 30 or above)
- Chronic neurological conditions that can compromise respiratory functions or the handling of respiratory secretions, or increase the risk of aspiration, or those who lack the ability to take care of themselves
- Children and adolescents (aged 6 months to 18 years) on long-term aspirin therapy
#The following citizens if only completed three doses, they are recommended to receive the next dose 90 days after 3rd dose free of charge:
- Uninfected individuals aged 50 or above; or
- Uninfected persons aged 6 months or above and
This table was updated on 18 October 2023, for real-time information, please see: https://www.chp.gov.hk/files/pdf/poster_recommend_dose.pdf
4.2 Seasonal Influenza
| Seasonal Influenza Vaccination | Recommend the following groups to receive the vaccine |
|---|---|
| Inactivated Influenza Vaccine (IIV) Intramuscular injection |
|
| Live-attenuated Influenza Vaccine (LAIV- nasal spray |
4.3 Pneumococcal Infection
| Pneumococcal Infection | Recommend the following groups to receive the vaccine |
|---|---|
| 13-valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV13) |
|
| 23-valent Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine (23vPPV) |
*The following are regarded as high-risk conditions:
- History of invasive pneumococcal disease, cerebrospinal fluid leakage, or with cochlear implants
- Chronic cardiac, pulmonary, liver or renal disease (except hypertension with no complications)
- Metabolic diseases including diabetes mellitus or obesity (body mass index 30 or above)
- Immunodeficiencies related to Asplenia, HIV /AIDS, malignancies or the use of systemic steroid
- Chronic neurological diseases that affect the respiratory function, causing difficulty in handling respiratory secretions, increased risk of foreign bodies entering the lungs, or lack of self-care ability
For details, please visit the following webpage: https://www.chp.gov.hk/tc/features/103165.html#10004
05. Special populations and vaccination
| Women in pre-pregnancy, pregnancy and breastfeeding | Persons aged 60 or above | Children and adolescents |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| Patients with malignant solid tumors | Persons with immune rheumatism | Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase deficiency |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
06. Comparison of infection, complication, and mortality rate after vaccination
- The total infection rate of the fifth wave of COVID-19 in Hong Kong was 15.8%, compared with among unvaccinated patients was 24.6%. The statistic illustrates that COVID-19 vaccines are effective in preventing infection. The overall fatality rate in this wave of COVID-19 was 0.71%, and the rate of death of unvaccinated persons infected with the COVID-19 was 2.87%.
- Statistics comparing the infection and mortality rates before and after vaccination against influenza and pneumococcal infections are not yet released.
The table below illustrates that three doses of COVID -19 vaccines are effective in preventing infection and significantly reducing deaths.
| Total infection rate of the fifth wave | Unvaccinated patients | Persons who have received three doses of Sinovac vaccines | Persons who have received three doses of BioNTech vaccines | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infection rate | 15.8% | 24.6% | 9.1% | 3.4% |
| Mortality rate | 0.71% | 2.87% | 0.04% | 0.02% |
The data in the table was released on 25th, Apr 2022 by University of Hong Kong. For more details, please visit: https://www.med.hku.hk/en/about-hkumed/knowledge-exchange/newspaper-columns/2022/apr/three-doses-of-covid-19-vaccines-prevent-infection-and-reduce-death
Prof. Gabriel Leung, Dean of Medicine, together with Prof Joseph Tsz Kei Wu, the University of Hong Kong, held a press conference on 22 March 2022 to update the public about the fifth wave of COVID-19 pandemic in Hong Kong. In the press conference, the professors mentioned that three doses of the vaccines could prevent 98% of serious illnesses and death cases!
The table below shows the effectiveness of vaccination in prevention of mild, moderate to severe illness and death for all age groups.
| Types of prevention | Age | 1 does | 2 doses | 3 doses | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BioNTech | Sinovac | BioNTech | Sinovac | BioNTech | Sinovac | ||
| Effectiveness in preventing mild to moderate disease | 20-59 years | 37.4% | 2.1% | 31.0% | 17.9% | 71.5% | 42.3% |
| 60 years or above | No evidence of effective protection* | No evidence of effective protection* | 71.6% | 50.7% | |||
| Effectiveness in Preventing severe disease | 20-59 years | 85.0% | 60.9% | 95.2% | 91.7% | 98.5% | 98.5% |
| 60 years or above | 65.6% | 40.4% | 89.6% | 72.2% | 98.0% | 97.9% | |
| Effectiveness in Preventing death cases | 20-59 years | 93.7% | 65.4% | 96.4% | 94.0% | 99.4% | Insufficient mortality data for calculation# |
| 60 years or above | 73.0% | 51.2% | 92.3% | 77.4% | 98.1% | 98.3% | |
*No evidence of protection effectiveness due to small or negative utility values and large confidence intervals
#Insufficient mortality data for calculation
The table was updated in 6th, Oct 2022. Source: https://www.med.hku.hk/en/news/press//-/media/HKU-Med-Fac/News/slides/20220322-wave_5_omicron_PHSM_update_final.pdf
07. Comparison of long-term effects before and after vaccination
The vaccines reduce the risk of long term COVID-19 effects in patients with mild to moderate illnesses. In addition, some studies suggested that COVID-19 vaccination improves the persistence symptoms of long term COVID effects.
- the vaccines reduce the severity of an acute infection;
- the vaccines may help the body to clear the residual virus faster.
Note: Statistics comparing the long-term effects of influenza and pneumococcal infections before and after vaccination are not yet released.
08. Precautions before and after vaccination
8.1 Precautions prior receiving vaccination against common infectious respiratory diseases (e.g., COVID-19, Influenza and Pneumococcal vaccines)
Consult your doctor before vaccination if you have the following conditions:
- You are allergic to any component of vaccines
- Have had a severe allergic reaction or breathing problems with any previous vaccines
- Feel anxious when receiving the vaccine
- Have a serious or unstable chronic illness
- Have a serious neurological condition
- Have a bleeding problem
- Have an HIV infection
- Children and adolescents who are receiving medications containing aspirin or salicylates at the same time.
- Have taken anti-influenza medication within the last 48 hours.
8.2 Precautions after vaccination
Common adverse reactions after receiving the vaccines against respiratory tract infections (e.g., COVID 19, Influenza, and Pneumococcal infection) include mild pain and swelling at the site of the injection for a short period of time. Most of these reactions subside spontaneously within two days. Some people may experience mild fatigue, fever, headache, muscle pain or chills.
- If you have had an acute allergic reaction to any vaccines or have had a severe allergic reaction for any reasons, please stay in the rest area for 30 minutes after receiving the vaccine. For others, please stay for 15 minutes.
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), mild to moderate side effects after vaccination are normal and usually disappear on their own within a few days. If you experience any abnormalities after receiving the vaccine, please report them to your health care provider.
Possible side effects after vaccination of BioNTech or CoronaVac (Sinovac) vaccines
1: Watch out for possible side effects after receiving the BioNTech vaccines
| Frequency | Side effects | % of patients possibly affected by the side effects |
|---|---|---|
| Very common |
|
>10% |
| Common |
|
≤10% |
| Unusual |
|
≤1% |
| Rare |
|
≤0.1% |
| Very rare |
|
≤0.01% |
| Unknown |
|
Cannot be estimated from available data |
2:Watch out for possible side effects after receiving the CoronaVac(Sinovac)vaccines
| Frequency | Side effects | % of patients possibily affected by the side effects |
|---|---|---|
| Very common |
|
≥10% |
| Common |
|
1% - 10% |
| Unusual |
|
0.1% - 1% |
| Rare |
|
0.01% - 0.1% |
| Very rare |
|
≤0.01% |
| Severe |
|
Detailed data is not yet available |
8.3 Statistics on abnormalities after COVID-19 Vaccination in Hong Kong
Until 31 August 2023 (inclusive), a total of about 20,847,200 doses of COVID-19 vaccines were administered. During the same period, the Department of Health received a total of 8,132 reports of adverse events following Immunization of COVID-19 vaccines. [Case rate: 0.04% (i.e., 39 cases per 100,000 doses received)], of which no fatal cases were related to immunization of COVID-19 vaccines.
| Total numbers of doses | CoronaVac(Sinovac)About 8,896,300 doses | BioNTechAbout 11,950,900 doses |
|---|---|---|
| Total cases of Abnormalities reported (cases/100,000 doses received) | 3,405 [0.04% (38.3)] | 4,727 [0.04% (39.5)] |
The above data was drawn on 31 August 2023, please check the real-time information: https://www.drugoffice.gov.hk/eps/do/tc/doc/Safety_Monitoring_of_COVID-19_Vaccines_in_Hong_Kong.pdf
09. Relevant government's information
9.1 COVID-19 vaccination programme:
-
https://www.chp.gov.hk/tc/features/106934.html
- Vaccine booking System:
https://booking.covidvaccine.gov.hk/centre/index_tc.html
9.2 Influenza
- The Government provides free or subsidized seasonal influenza vaccination programme to eligible persons and to encourage people aged 50 or above to receive the vaccines.
- For more information, please visit the following website: https://www.chp.gov.hk/tc/features/18881.html
9.3 Pneumococcal Vaccination Subsidy Scheme 2023/24
- Since 2009, the Government has been providing subsidy for Hong Kong residents aged 65 or above who have not received pneumococcal vaccination to receive one dose of 23-valent polysaccharide pneumococcal vaccine (23vPPV). Starting from 2017/18, an additional dose of subsidized or free 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) has been providing to older adults aged 65 or above (who are at high health risk).
- For more information, please visit the following website: https://www.chp.gov.hk/tc/features/103165.html#10004



